To get back to fleeing individuals in the Ukraine-Russian War: the fleeing of the young people is designed to represent the loss of infrastructure for military means and is in that there is no order from a kurtosis leader but an individual decision. This is common when one group has unlimited power or almost unlimited power. When the control group is the same as the group that holds unlimited power, such as the nursing home deaths due to COVID-19, one sees the older group’s ends being rationalized and carried out. Whereas if the group has no power or at least very little power, the ends are dispersed. We can see this by the difference between SINDY RL and PCA: if the SINDY RL is adequate then the group which holds power will succeed, and if not then it will fail.
This means that we must discern what the scarcity of the dominant Cultural System is as against the PCA of the rising logical system. This is because there will be an overturn which can be measured through a PCA which shows the basis in a marker. It is not therefore the number of fatalities. Can we connect it by the ratio of the number of fatalities to the ex-migration? Remember that the Russian goal is to drive out or incorporate a large number of Ukrainians so that they can then use attrition in their favor.
But again, unfortunately, there is too little data to make such a comparison. This is not unusual in any field where the measurement is still not able to be defined in all cases. However, this may not be for very long because organizations are trying to assess the damage that has been done to civilians. A simple case is the International Rescue Committee, which takes the data of Russia “relocating” children. What is important is that this number is small compared to the number of internally displaced, refugees, and fatalities. Therefore, the number is sufficiently small to do statistics as to what Cultural System is being employed by the Russians on Ukrainian civilians.
Why this is important is that like ratings numbers in black-and-white and color television sets, a small number can be used to magnify the whole of the population. However in this case the “ratings number” is somewhat different in nature. Indeed the International Criminal Court has issued arrest warrants for President Vladimir Putin and Russian Children’s Rights Commissioner Maria Lvova-Belova for “unlawful deportation of population (children) and that of unlawful transfer of population (children) from occupied areas of Ukraine to the Russian Federation.” This means that we are getting to a specific mathematical expression which shows the dominant Cultural System that runs the Russian side. If we can get an equal Cultural System for the Ukrainians, then we can produce both a PCA and a SINDY RL and tell what the changes are.
We again must point out that the nature of Cultural Systems is that they are Xaotic, and even within the Cultural System a large number of possibilities are likely because they only need to hold to the Cultural System as it is known to its population. Since the dominant Cultural System is in the hands of a few, then the Laplace transformation can have large divergences as a Xaotic system.
What we are trying to do is balance an internally driven sigmoidal curve with an externally driven sigmoidal curve. The two components are the externally driven refugee dynamic in both the state of Ukraine and the state of Russia, against the displacement of Ukrainian children to Russia and the Russian-speaking citizens of Ukraine against the proclaimed Russian and next territories in Crimea, Donetsk, and Luhansk. The idea is that people are torn away from the nationality which they identify with both externally and internally driven. The question is whether the sigmoidal curve varies between the two nations and in which forms.
This means as with the black and white versus color television scenario we need to find a time-delineated chart. The first chart shows that of the original invasion starting in 2014 and ending in 2021 versus the current invasion, there is a striking distance between the original invasion, which generated very few refugees, and the current phase of the invasion, which generated 5,000,000. In fact, 2022 generated a wave of refugees while 2023 generated only a fraction. It is also to be noted that 1.27 migrated to the Russian Federation while 2.2 million went to only three countries in NATO: Poland, Germany, and Czechia. In addition, 1.3 million went to other countries and only a tiny fraction of these were to Russian Allied states. The vast majority were refugees: 5,865, 447 with only a tiny fraction being asylum-seekers at less than 40,000.
This is interesting but what it conceals is vital: we do not have enough of a time plot to measure PCA. What we do have is enough to confidently show that 20% of the refugees went to Russia and its allies, while more than 80% headed to someplace else with NATO being the overwhelming destination.
What this means is that there is enough data to point to a mathematization but not enough to form a model. It does show that this avenue of approach will be possible in a few years just as the black and white versus color took a bit over half a decade to be adequate. However, drilling down into the numbers of the United nation High Commissioner for Refugees gives a deeper look into the data. But this too is not correlated. Which means that one day it will be, but not yet.
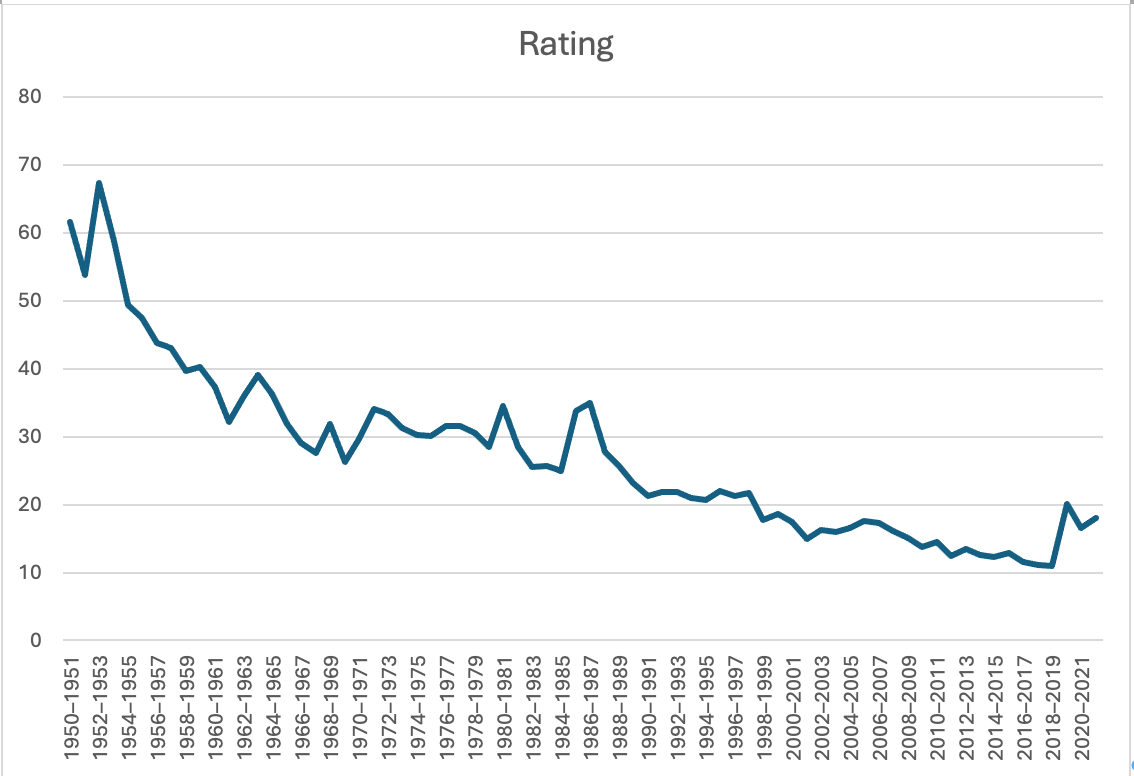
Contrast this with a simple example that shows the trend from Postmodernism to Digitalty the same way that black and white to color showed the transition from Modern to Postmodern: the fall of network television. In fact, we can determine the division between Modern, Postmodern, and digital in one chart. The first is the highest-rated show on television.
(From Wikipedia with minor revisions for clarity. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_most_watched_television_broadcasts_in_the_United_States)
Which gives us a graph:
Showing the steady decline of the Modern and the transition to the Postmodern in the late 1960s, and then the decline from the Postmodern until the Digitally takes hold at the end. This shows quite clearly the decline of dominance, first quickly as the Modern gave way to the Postmodern and then a slow decline once the Postmodern had established itself.
But there is more to be gained from this chart than merely the ratings. And that is the prevalence of what kind of show is popular at any given time.
Then why did I go from war to television ratings? Because if the data is better off being hidden, such as the casualty counts in a war and the refugee numbers, then it will be some time before the numbers will be made clear. On the other hand, if there is money to be made by publicizing the data, then it will be publicized and, in fact, will often encourage some company to erect a means to do so. This means that war is hidden because the raw facts of the conflict are often unpleasant to the country that is participating in the war. Whereas counting eyeballs is always profitable. This is why the search was done in the way it was: to show that important data points will be hidden.
Indeed, there are many insights that can be seen from the charts. A simple example is that when looking at the single most watched broadcasts almost all of them are from one single place: the Super Bowl. This can explain why at the end of the ratings, the most watched broadcast is of football in preparation for the Super Bowl. This means that the readings can be shown to be the Postmodern watching television.
When we look at other media productions one can see that there is a shift from a picture of an event to the use of the studio as the essential part of the production process. Do not think that this is not present in the Super Bowl, because the venue is a studio for a particular use: broadcasting a football game. There is no other reason for the venue’s existence, is not a street with things going on in it otherwise, but instead is a structure designated for a particular broadcast.
A simple example is in the world of rock music: when the foremost bands started to use the studio as part of the process, it changed the production from a Modern to a Postmodern setup, and this means that the digitization of that production is a change from the Postmodern to the Digitality. We will discuss the Modern to Postmodern in the next section, but they should spend some time on the Postmodern to Digitality step here. This is because while the digitization of content is not the most popular, it is the most relevant to the discussion about TV production, and this to is normal: the φ of the older Cultural System is far more massive but also is well understood, whereas the Kurtosis of the newer one is not well understood and therefore needs far more discussion in order to be executed. An example would be that Mad Men, Peaky Blinders, The Handmaiden’s Tale, Orange is the New Black, and Mindhunter, as well as others, are the most talked about even while they stand a new chance whatever of being the most popular. This is the difference between the end of the Postmodern and the beginning of the next era.
What we have is a Postmodern view, which we need to be mathematizable, and a Digitality view that needs more work in this direction. This is because the postmodern view was formed in the late 1970s. this view is that labor is taxed to little and capital gains are taxed too much. But remember that in the late 1970s and early 1980s, various forms of stock measurement showed exactly the same thing: there was to little money in capital gains to support the valuation of stocks. Thus Reagan pushed down the capital gains tax rate, and a boom then established itself. We are now in the reverse situation: the capital gains tax is too low, the labor tax rate, that is FCA and income tax at the bottom is too high, and thus the bottom 90% of the economy does not have enough to purchase the necessary goods which the society needs them to purchase.
One of the largest markers that Digitality has made tremendous strides is in the two elections of the United Kingdom and the United States. The United Kingdom while its leaders were younger, the voting age population changed from the baby boom to a younger set: the old government was Conservative while the newer government was Labour. The change in the United States was even more dramatic because the Democratic party’s initial presidential nominee was President Joe Biden, but a revolt happened when it became clear that Joe Biden, who is from the early part of the Wartime Boom, gave way to, Kamala Harris who was between the Baby Boom and Generation X. these changes in the government of two of the largest nations shows that a change was occurring, though more slowly than the Modern.
The reason that the revolt in the US was important is that it overturned the old system of nominating a president: in the postmodern era primaries or caucuses were the defined way that a president was nominated with the convention being a seal rather than a real process. However, in the interval between the primaries, all of which were won by Joe Biden, and the Democratic convention, a revolt sprang up and Joe Biden was forced to resign his attempt for a second term leaving the position to be occupied by the Vice Presidential candidate. As of the first writing of this book, it is not clear what the process will be like in four years time, but it is clear that changes will be made. Partially because the accelerated presidential campaign has a unique freshness that the older postmodern system did not have. Because politics is about compromise, it seems likely that the primary system will be modified to capture the freshness without completely eliminating primary and caucus as the way that voters can express themselves. Part of the problem is that primaries are slanted by the parties so that the primary is not really the key choice but who runs in the primary. This is seen by the fact that 67% of Democrats felt that Joe Biden was too old to run and yet he still managed to run the table of the primaries. This distance between the feelings of the electorate and the winners of the primaries is large enough that something needs to be done. And it will be in a new Cultural System.
The mathematics of the US system shows the curve at the end of the postmodern, which told one party, the Democrats, that they needed to change candidates. This is exactly what the Graph on page 122 predicts: there is not enough room on the postmodern curve, and thus the Democratic Party made a change to their nominee because there was no borrowing to be done within the postmodern system.
It should be noted that where borrowing is allowed, it will be taken advantage of, where borrowing is not allowed is the point of stress. Because the Cultural System determines when borrowing is allowed and when it is not, there may be a shift to a new Cultural System. But then the question is does the Cultural System allow the society to work in its current form? An example of when a Cultural System was proposed and failed is during the Watergate hearings: the Nixon administration needed to borrow popularity for the coming election of 1972. And the popularity was borrowed to win the 1972 election but there were enough nagging questions that a few reporters opened up the can of worms and the system collapsed. But there were still problems and it would take two more presidential elections to resolve these problems.
Definitions of Markers and Periods
We also must describe what the difference between Visionary, Revolutionary, Evolutionary, Late Phase, and Nostalgia is, because each of these definitions are different.
When the case is for a visionary ideal, being personal is paramount. The same can be said of Lord Kelvin’s theory of electricity: the immediate problem was feedback as close as possible to the cables rather than having to wait. So, the visionary point is to have immediate feedback from whatever equipment was used. A simple example of this is how in filmmaking making the standard has already changed from analog to digital, and this change affects all sorts of changes in the filmmaking industry. The difference is that rather than looking for a current cultural system, the visionary is looking for something different because the current Cultural System has already shown itself to be unworkable in this particular instance. That is, the visionary sense has played out the current contemporary Cultural System and is looking for and alternative. Since there is no way to do this in the current contemporary model it has to be done ab initio.
Revolutionary is quite a different creature, in that there is some standard of performance which the new Cultural System can provide more quickly or with some other advantage. It also takes into account that there are a large number of people who are looking at the way of capturing results, and this itself forms a kind of feedback loop because a number of individuals is in itself a measure of success. Thus, Revolutionary is opposed to another standard. But this means that revolutionary activities can be before the entire structure is ready to be ensconced as the Cultural System. Taking some random examples Impressionism began as a search for plein air without reference to how many buyers would be for the paintings, eventually, this needed to be solved but it was hoped that the expression of light captured on the spot would be enough. In the early days of C and UNIX, the primary qualification was to compile programs in real-time rather than on punchcards. The reason for this was to have immediate feedback from the computer. Again, eventually reasons to by such machines needed to be expressed, but originally the idea was to have as close to real-time feedback as possible from your computer. This means that while Digitality is not general it might be in specific areas, just as while the President of the United States may still be Postmodern, there may be others who are already looking at affairs in a different way.
Evolutionary supposes that the system has been ensconced as the dominant system and the problems are to unify all of the problems in a new way. The example is from the Neoclassical Period and the creation of a full electromagnetic theory by Maxwell. One of the distinctions between this and the revolutionary period is that a totality must be shown within the Cultural System. This means that the revolutionary period can make advances because and is assumed that there will be some totality that needs to be understood, whereas, in the evolutionary period the totality must be described in full.
The Late Stage is the point where exceptions are in place and new ways of applying the Cultural System need to be found. A clear example is just before the Great Depression, when it was clear to almost everybody in the developed world that the means of maintaining a monetary system had collapsed but the attempts were not always to effect the new but often to maintain the old in some way. When this period collapses it is likely that a revolutionary period of the next Cultural System has begun.
Nostalgia supposes that the Cultural System represented has in fact died and individuals are mining the depths of what was passed and is it possible to still live in the previous Cultural System. There are even groups that maintain the previous, or earlier, Cultural System such as the Amish of Pennsylvania.
With this list, we may now start the process.
Digitality Markers
One problem with setting forth the markers for the present era is that since it is not complete many markers have not happened or are only faintly recognized. But the visionary markers and the coming revolutionary markers have some validity. It is here though that we must disentangle the Postmodern markers from the Digitality markers. In the Postmodern universe, the markers still pointed to an analog era which more and more picked up a digital aspect.
Thus, we need an algorithm to sort out the extraneous events from those that mark the change that we are looking for. In this sample example, the main thrust is how information becomes distributed and how that makes discoveries possible once the mechanism is known. The second question is how different aspects of human intelligence cascade even though the movements are quite different.
This means that C/UNIX/SQL started out as Postmodern markers, and only gradually with the introduction of Linux, the proliferation of C as the core language of operating systems, as well as the widespread use of relational calculus did they become Digitality markers.
The primary difference is that Digitality does not need the transition from the input to the output to be human readable, and this is shown by Neronetworking where the transition is black-boxed, while in the Postmodern it is represented by a chain which can be understood as human readable even if no one actually does the calculation.
When does the Digitality movement start to have a visionary aspect in that we can establish markers? The obvious answer is when college graduates decide that it is better to form a company than to continue on the University program: Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Bill Gates founded their companies in 1976, with Apple, and 1975, with Microsoft. This means that a marker can be established by the simple use of founding dates as a way of making mathmatizable the rather messy process of developing software and hardware.
When a protocol referred to as TCP/IP was developed as a networking protocol by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn in a first-generation form in 1973. When it was chosen as the common protocol or ARPANET, which was the forerunner of the Internet, we can then bracket 1973 through 83 as the era of a “Visionary” timeframe because the idea of a desktop computer, the software written in C rather than assembler, the core programming for SQL, and a networking protocol which allowed computers to be connected even if they were desktop computers had been formed.
The other marker is the discovery of the impact that destroyed the dinosaurs, in that in the 1960s it was still believed that the dinosaurs were cold-blooded and confined to muddy lakes to move their enormous weight. This is because cold-blooded creatures cannot wonder about on land and there was no reason for them to be extinct. However, in the 1970s there was a movement that pointed to geological structures in fossils that were better explained by being warm-blooded and that the avians in fact dinosaurs, and the Alvarez Hypothesis main the hypothesis that a very large asteroid impacted the planet which caused the non-avian dinosaurs to be extinguished. This led to a very different picture of the dinosaurs as being warm-blooded and spending from pole to pole in their reach. This again made a marker that changed paleontology. While some paleontologists still want the nature of warm-blooded and cold-blooded to not be an issue, this is only because warm-blooded and cold-blooded is not directly found in fossils, but there will be obvious markers of the level of warm-blooded and cold-blooded in the bones as an indirect marker. Warm-blooded many are not visible but signs that it is there will almost certainly be. For example, hollowing out of bones is not an issue for a cold-blooded creature, but is vital for warm-blooded creatures who want to lighten the weight that is being carried around.
These markers show that somewhere in the mid-1970s to early 1980s visible markers became obvious that a new Cultural System was being developed. But it is still within the context of a Postmodern system though it becomes stronger with time and with the influence of economic factors. More and more, the technology sector is being networked and the combination of networking and computation dominates the working world.
It is then necessary to bring mathematics to the table in the sense that there was a different way to treat computers which was different from before. Instead of being graspable by discrete calculus, as was the case in the Postmodern, the idea of formulating trees and other forms of data that were more compatible with the idea of a tree, such as the B-tree, and of the table, in the sense of a SQL table, began to change how we structured data from a peer amid to a table which related to other tables.
The moment when research and defense-oriented networks became open to any form of industry, and it needed to have a common way of representing data which became HTTP, is the obvious marker.
So how do we work through being mathematizable?
The problem is that a complete matrix is unavailable. Thus, we must use a sparse matrix.
We can then use the ordering to find which factors of X are the most strongly aligned. This may seem obvious, because after all one can write software but it is only valuable if you have hardware to run on it, and you need an operating system to implant the program or application with.
That is also logical that people on the ground at the time they are working have a good idea as to which ideas will be fruitful, even though they may miss some in the hurry to put out their product. For example, if one proposes a giant impact asteroid then one passes to look for where it is, and this leads one back to the strata to find where there is a rich layer of iridium - that is the element that is highly likely to be from an asteroid. One can measure the iridium at various points on the globe and see where the iridium is at the largest concentration.
This means that networking, hardware, and software form a unit that can be examined at the time. Similarly, the asteroid impact hypothesis leads to a question as to whether the layer between the Cretaceous and the Paleogene (K-Pg formerly K-T for Cretaceous-Tertiary) shows a pattern that is only to be associated with a large asteroid impact.
This means that taking as a sparse matrix layer is not merely a tool but the way that many people will survey the landscape of their field. This means that the marker layer is not just a tool but a way of simulating how people at the time were looking for ideas. In short, math is not just a tool but a method for mimicking how people would search for ideas.
The problem is that what the minimum of m and n are is not precisely known and has to be searched for in a real-time search. That is, min (m n) has a definition that is to be found by real-world applications.
Note that this has both a real component and an imaginary component, meaning that there is a theoretical limit as well as a practical limit.
This means that a cluster of similar events shows a marker if the events are of a high enough value. The value that is currently used is 6σ, which means that our next challenge is how to establish 6σ. unfortunately, as of this writing, there is no generalizable function, and instead, the 6σ must be chosen for each available object.
Again, the reason for this book is to expand on how the Postmodern era is in Late Stage and a new vision is taking shape. With the global crisis of 2007 through 2009, it was fairly clear that the Postmodern age was in Late Stage. This was a deeper recession than any that had taken place before and it had no warning. Essentially, various weak points of the financial system were piled up and collapsed. The solution, in part, was to make residential real estate open to commercial investment, which eventually caused the price of homes to boom. Because the Postmodern state did not want to interfere, no government program to build houses was put in place. The result was this was very good for the people who owned homes and very bad for the people who did not own homes.
But rather than tackling the problem with the building, major parties in the US were committed to protecting the assets of the older population. This led to a campaign that had two very distinct groups: those who wanted their assets to be protected and those people who were not in that asset group. There were just enough Baby Boom constituents to make this so even though a large fraction of the constituent class was unrepresented by the presidential candidates.