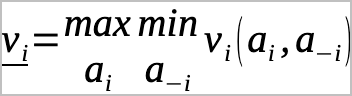Introduction
When introducing the first Cultural System one faces a breakpoint in that there has been no Cultural System yet proven. The first division is does one starts with the Cultural System which begins the train of Cultural Systems that culminates in the present or does one starts with the Cultural System in the present and works backwards to where it began? The first way is the most logical but has the problem of starting in the middle with no real explanation as to why it began where it does and with no explanation as to why it will culminate with a change at the present time. In short, while it starts at the most logical place it does not answer why this is the most logical place for it. The second route is somewhat like a blog: it starts in the present time with an explanation as to why it does so and explains what the present conflict is that erupted. It then goes backwards until there is the beginning point that can be explained by looking forward and showing how the beginning crisis will lead to an unfolding in the present. This means that the first will be the logical place, but it first needs to be unfolded in the second because it needs to show how a Cultural System enhances the practice of history. It also has the advantage of naming the eras and only then explaining why those names are most obvious for the given logical system.
It should be pointed out that there are many Cultural Systems and that in any given period there will be the ending of a Cultural System and the installation of a new one. At any given time, there is a crisis that needs to be elucidated by what cycles in logic are changing. Thus, in the 1980s there was a change between the analog means of distribution of data and a digital one which was becoming common and would be the dominant form in only a few years. There was the computer revolution with its operating system wars, a disagreement on how one should program in this digital world, and subsidiary things such as what would be the database that would act as the repository. All of these questions have largely been answered and other Cultural Systems have taken center stage.
In this particular moment, there are changes in the way information will be distributed which is different from how it would be stored. There are also seemingly unrelated questions that also need to be changed. These unrelated questions are part of the Cultural System just as the USSR disintegrating was in fact part of the digitization of information. The fact of the matter is that Cultural Systems are signaled by a conflict between segments of society. This conflict derives from a deep Cultural System that needs to be explained. The 1980s was the period between analog and digital, it was also the period when a new kind of writing about the information system became prevalent. Postmodernism became common but it was almost unused in public discourse. This captures the sense that at any given moment there is a crisis, and several people will be able to describe what they see as the crisis and what should come after it. The answer is there is always a crisis, the crisis has many sides to it, and there are many answers to the question. Then the crisis is resolved, and a new crisis appears, and the same cycle repeats itself with the new crisis being center stage. This pattern is how Cultural Systems establish their presence: where the old way of thinking lasts it will not appear as part of the crisis, where it does not it is argued about, even fought over, in its various forms.
In the present time, this book will label the current ending form of logic “Postmodernism” and show why it is dying and a new form of logic is coming into being, which this book will label “Digitality.” It will start by describing why a new Cultural System is present and will show how the tendrils of its existence have been brewing for some time. This is also part of a logical system: fragments of it will be present but they do not seem to be a threat. An example would be the assembly line, it started with very small pieces of work done on assembly such as cans for various consumer goods, and was developed into a very fine art by Henry Ford first the Detroit Automobile Company, which was founded in 1899, and then as Henry Ford Corporation, founded in 1901, which was then reorganized in 1903 as the Ford Motor Corporation. The Detroit automobile company would eventually become General Motors, meaning that two motor corporations would come from Henry Ford. The assembly line was key to the Modern logical system, but it developed under a previous Logical System.
This means that 30 years from now there will be a different Cultural System which people will be concerned with, and rightfully so. And the same work of identifying markers in this new era will be done again. This means that history will continue to be the exploration of data and lives, but it will also have stacked on top of this, based on Vector Algebra and from the language of history, to make mathematics explain how the Cultural System changed. This is because a Cultural System that works will not be fought over except on the edges of people who see faults with the current structure. However, there will be wide disagreements that will show up as economic, cultural, social, and structural issues that need to be debated because it will then be clear that new systems will have to be introduced.
At the end of each Cultural System the mathematics for when the major markers are laid out for the era. Remember that each Cultural System is a merge rather than a sharp break, but certain markers will be more significant because of the moment. But very often this is because of cultural weight rather than true significance. For example, the assassination of JFK is often listed as an extraordinarily significant moment. But this resonance is not a change of direction or a new Cultural System, but a common marker in the brains of a large number of people. Remember that JFK was narrowly elected and was unsure of how to use the mechanisms that were given to him. Early attempts to carry out the programs set by his predecessor were disastrous such as the Bay of Pigs invasion of Cuba, which had been given a green light by Eisenhower. This is not just that it was in retrospect but that it was now seen as different in the different programs then enacted, such as the Moonshot program. Such moments do not make enormous sense in this example Cultural System, but may in other Cultural Systems in that they may well be a marker of the coming of age of a new generation or other signs of a change in marker.
Digitality
Crisis
Every age is born in crisis. However, the shape and nature of the crisis differ. This means that we must work out the Cultural System which is Late Stage and the new Cultural System which has become Revolutionary. Because there are often charts and figures for the Cultural System in crisis, and there are often manifestoes for the Cultural System that is coming into being a paradigm is set up where there seems to be an antipathy even an antagonism which seems to be formed from the hostility of the two Cultural Systems and indeed between the different eras which are arrayed against each other. This is not the case, what is the case is that there is an older Cultural System with an older group of people and that group of people knows the ins and outs of the older Cultural System and therefore is reluctant to change. At the same time, there is a newer Cultural System which to the young seems almost second nature because they were born underneath this Cultural System and reflexively create the new creations of the epoch, not always with glee but because they understand how the new Cultural System both gives and takes away. These two systems are arrayed against each other because there are two groups of individuals each one knows the internal mechanisms and reaches out to the world with those internal mechanisms as a ground point.
One of the clear points is the greatest threat to society in general. In the Postmodern era that threat was the global thermonuclear war. It shows up in the cinema, the foreign policy, and in almost every form imaginable. Consider that NATO is the preeminent military alliance and sets Article 5 in place:
The Parties agree that an armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America shall be considered an attack against them all and consequently, they agree that, if such an armed attack occurs, each of them, in exercise of the right of individual or collective self-defense recognized by Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, will assist the Party or Parties so attacked by taking forthwith, individually and in concert with the other Parties, such action as it deems necessary, including the use of armed force, to restore and maintain the security of the North Atlantic area.
This is slightly obscure because the phrase nuclear weapons is not mentioned merely “armed force” which deflects the nature of the armed force. But on the same site at https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_50068.htm it makes it clear that nuclear weapons are intrinsic to the alliance.
This structure was laid out before the USSR had tested a nuclear weapon or even an atomic one.i This means that before there was a solution to the threat of nuclear weapons it was decided that among the many threats of the post-World War Two regime, nuclear weapons were a part of that structure. Grappling with this problem however made it clear that it was not simply the next iteration of total war, which was the threat that World War I and then World War II laid bare as the Modernist problem. This means that a change in military strategy is only the beginning because there needed to be a mindset for strategy which was different than total war. Total war engulfed France in 1940. While there were casualties the infrastructure of society remained largely in place and the individuals who survived basically knew how the occupation was to be established. The entire event occurred in approximately one year from the start of hostilities.
Global thermonuclear war can last less than an hour. The infrastructure that girds society is largely in ruins. The members of society are either obliterated, sickened by nuclear effects, and they must live with those effects for a very long time. In other words, the scale of the event and its effects are quite different. Fortunately even before the event occurred, which we remember now as the Trinity test, a branch of mathematics was being formed that would be the basis of postnuclear warfare: the branch of logic was “Game Theory” and its authors were John von Neumann(1903-1957) with help from the economist Oskar Morgenstern (1902-1977). The original idea came from von Neumann and a paper in 1928 that proved the minmax theorem for two opposing players which essentially says that player one’s best response to player two’s best move is V and player two’s best response is -V. Or:
With:
i being the index of the player
-i being the index of the opposite player
ai being the action of the player
a-i being the action of the opposite
vi is the value function of the player.
Think of this as a game of chess where all information is known to parties and there is a value for the moves, that is zero-sum and perfect information, that a player will make which depends on the best sequence of moves that their opposite number can make. In other words, it is a turn-based solution to a two-player game.
There have in a number of other elaborations on this proof even beyond the basic book, Theory of Games and Economic Behavior in 1944. This means that while the atomic bomb was being developed the structure into which it would be placed was also being developed. There must be a math to which real actions must be placed.
Von Neumann remarked that this was the key to the field to the point where if this theorem were not proved there would be no point to go any farther. And remember, Von Neumann is one of the great minds of the 20th century, so his weight carries a great deal of significance.
The question should be asked why I am explaining this in the Digitality era rather than the Postmodern. The reason is that the challenge for Digitality is not a two-person or n- person game, but a one-person game where the future is the opponent. Or in another term, it is individual against nature rather than individual against individual. Instead of an opposite number, which you will note is assumed in the minmax function, it is the rules itself. Climate change is not another person but the nature of the game. This means that the attempts to blame any given group of people are in a sense the attempt to not blame the individual who is making the accusation. For example, if a middle-class “Western” person tries to move the discussion from consumption to production, they are attempting to remove the claim from their own consumption which is much higher than in the developed world. In one sense the accusation is true: the middle-class person does indeed produce less carbon than the more well-to-do person, but on the other hand, it elides the larger difference between the middle-class level of consumption with that in for example Nigeria. The gag is that the middle-class person in the West is going to be reduced because the wealthy people will demand reduction and will conspire to make it so that the middle class cannot afford to be middle class.
Note that this engenders a specific notion that is subliminally present in person versus person, but instead of the rules it is the competition itself: we want to profit in the short term but that comes with the cost of not having a planet to live on. Realize that the earth will survive, but the way in which populations of individuals in a grouping which surfaces many variables, is less certain and more astringent. Basically, the people who own the resources, which is in itself a nonsensical construction, can borrow from the future the resources that they will admit as “profit” today. This is the conundrum between what the law says and what science says. Inevitably, the law will have to conform to science, but it can take a great deal of time to do so. And in fact, there is an example: slavery. Slavery was abolished three times in the United States’ history: once it was taken to be a de facto result of the economic system. However, the cotton gin reprieved the system because it made reducing cotton much less expensive. The second time a Civil War was fought, the result was the post-Civil War amendments. But this too was not the end of things because while de jure slavery was banned, the world of the South continued onwards with two classes of people, one of which was subservient to the other even though the law says that the two groups were equal. In terms of a Cultural System, everyone realized that two groups of people were not equal but made noises that said that the law regarded them as equal. This only changed when television came into the picture because then other people could see the inequality and they could not unseat it.
This is the power of a Cultural System: it is one thing to know but it is another thing to see.
A good example is the removal of Pres. Biden from running again.
This can be seen at three levels: one is when he ran the first time, and rumors that he was going to be a one-term president were circulated. There were a few people looking at the data for how long a president could serve and realized that the chances of eight years of Pres. Joe Biden was unlikely. However, these few rumors were not endorsed by Joe Biden and when the time came, he announced that he was running again. So, the first lens is from history, but it is neither exact nor 100% assured.
That is when the second level happens: seeing the president as a reporter, it became relatively obvious about a year before election day actually happened that the president was not going to be among the survival population. When this happened was a matter of debate but it was clear in November 2023: President Biden had lost at least two or three steps and this was noticed on the other side. The problem is of course that his close associates and his deepest supporters were not going to listen. This is the point where ideas were circulated as to how to replace him. Some brought up the idea of an open convention, while others took the line that Pres. Joseph Biden could pick Vice President Kamala Harris to succeed him. The second level is seeing the Pres. and realizing he was not going to make it. The problem is that this is not enough to persuade enough voters because the primary voters are old. And they do not wish to hear that they are old.
This leads to the third window: not the president as he has but the president on the news. Even this would not convince the diehard supporters, but it would convince politicians and donors and convince many who were watching various forms of figures, or if one wishes to think of this as “tea leaves” one may be forgiven for it, who also saw in their own small sphere that Joseph Biden was not going to be reelected. As Isaac Asimov might say: “You only have to watch the media.”
But doing this is a tricky problem: the people who need to be convinced are not supporters. It is enough of the supporters who need to be convinced however it is the non-supporters that one must reach. This is a conundrum where the newer wave of Digitality has to be influenced by the older wave of Postmodernism. This is because the older wave is still in physical charge of the decisions, but the younger wave is in charge of the actual mechanics.
This means that a matrix must be set up where the old supplies the data but the action must be from the new. This means that while the president secures the maximum support, it is not the majority of support. The new form of the Cultural System needs to be at the minimum. This means that the minimums are here when the election is closest. This “maxmin” formulation will be examined later.
But it means that the very words used are changing. For example, let us that take the campaign speech of Harris:
And then let us take a 2016 speech by Trump on his campaign:
The difference is striking especially when you consider that Trump was reelected on his cluster of words which placed Hillary Clinton and a future that looked to the past. It was also about “jobs” which was an important feature in Trump’s campaigns. The focus of the two speakers was much alike but also very different: Trump talked about what he was going to do to Hillary Clinton, and Harris focused her speech on what the people were going to do. In other words, Trump took center stage where as Harris was going to lead everyone. And remember, Trump was the winner.
But this did not rest on his rhetoric, bought on the promise that he would hold to a postmodern economic theory that had been proven. But this is something that can be examined as to whether the logic is sound.
The problem is That the economics are from the present expressed in the past: the capital can be expressed as the surplus of the value produced minus the cost: p = s – c and we must account for the interest: p = s – c – i. We can then account for the finance cost for the future under i. If this sounds like it is simple, it is simple in theory but not in practice, because money that is available this instant has a powerful urge to be spent. But all of these numbers are at a present value. However, the work to be done for all of them is a future value. And as the old saying goes: “Predictions are difficult, especially about the future.”
What this means is that there is a huge past bias in addictions about the future. This is why the linear algebra that was constructed was useful: not only in economics but in all forms of human activity, the two dominant ideas are the known past and a predicted future. And the predicted future is slippery and hard to pin down.
What this means is that the present economic circumstance and the present ideas about the future can be held onto until there is overwhelming evidence that they are wrong. This is why society advances quite evenly forward until it reaches a collapse in some areas: the harder the collapse the more desperate people become to find a way forward. This concept will be referred to as the “past bias” and it is seen in the Fourier and Laplace transforms, both of which have a future correction to the past bias. The sigmoidal curve collapses when that future correction becomes more than the past can hold back.
i This book uses atomic to mean a fission weapon and nuclear to mean a fusion weapon.